Exercises 7.9-7.21
7.9: automatic code formatting
In the previous parts, we used ESLint to ensure that code follows the defined conventions.
Prettier is yet another approach for the same.
According to the documentation, Prettier is an opinionated code formatter, that is,
Prettier not only controls the code style but also formats the code according to the definition.
Prettier is easy to integrate into the code editor so that when the code is saved, it is automatically formatted correctly.
Take Prettier to use in your app and configure it to work with your editor.
State Management
For exercises 7.10-7.13, you can do the state management either by using:
- React Query and Context
- Redux
You can maximize your learning by doing both.
7.10: State Management, Step 1
Refactor the application from using the internal React component state to using one of the above technologies for the application's state management.
For example, you can refactor the app to use the useReducer hook and context to manage the notification data.
Change the application's notifications to use the state management at this point of the exercise set.
7.11: State Management, Step 2
The next two exercises are quite laborious but incredibly educational.
Store the information about shows in one of the two state management solutions.
In this exercise, it is enough that you can see the shows in the backend and recommend a new show.
You are free to manage the state for logging in and creating new shows by using the internal state of React components.
7.12: State Management, Step 3
Expand your solution so that it is again possible to like and delete a show.
7.13: State Management, Step 4
Store the information about the signed-in user via State Management.
Views
The rest of the tasks are common to both the Redux and React Query versions.
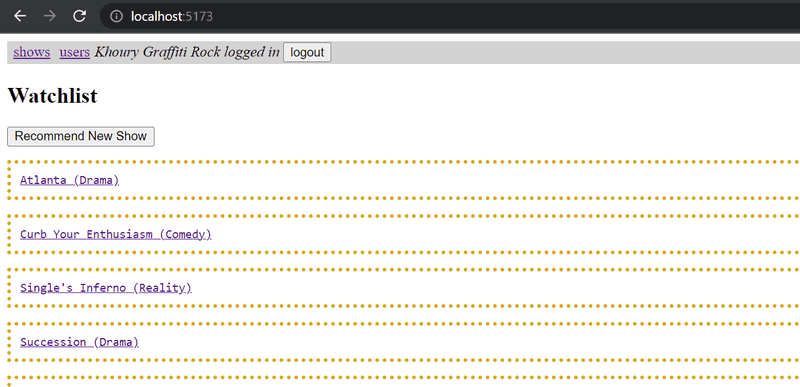
7.14: Users view
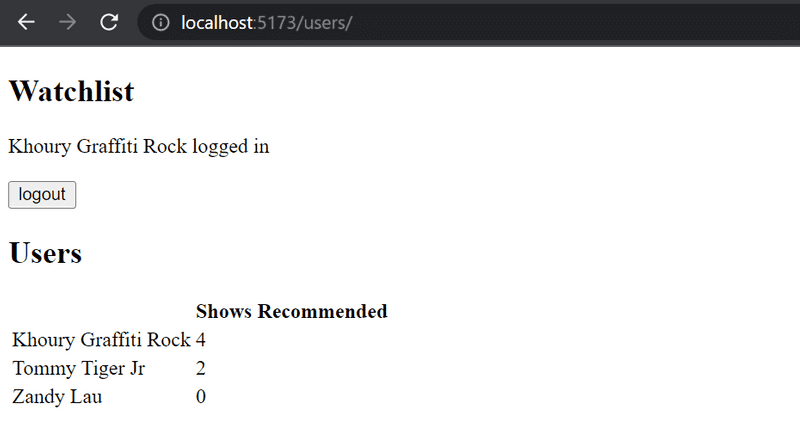
Implement a view to the application that displays all of the basic information related to users:
7.15: Individual user view
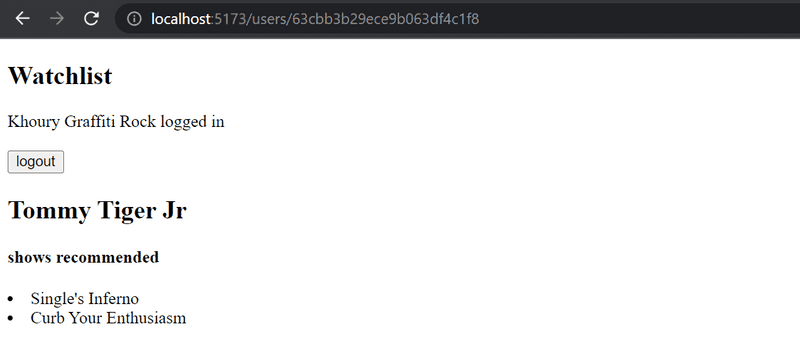
Implement a view for individual users that displays all of the shows recommended by that user:
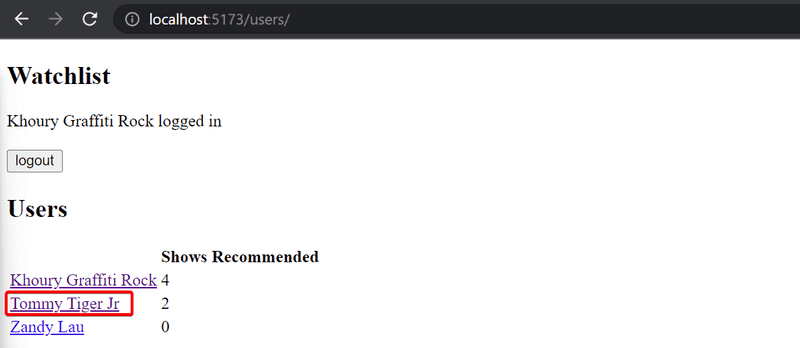
You can access the view by clicking the name of the user in the view that lists all users:
Pertinent: you will almost certainly stumble across the following error message during this exercise:
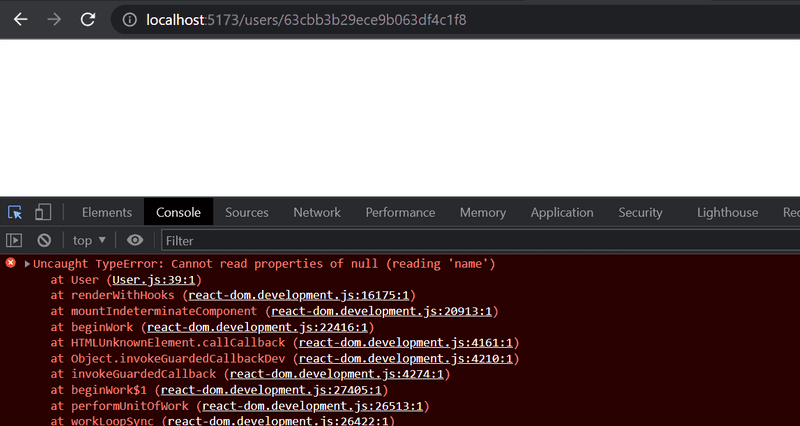
The error message will occur if you refresh the page for an individual user.
The cause of the issue is that, when we navigate directly to the page of an individual user, the React application has not yet received the data from the backend.
One solution for fixing the problem is to use conditional rendering:
const User = () => {
const user = ...
if (!user) { return null }
return (
<div>
</div>
)
}
7.16: Single show view
Implement a separate view for show.
You can model the layout of your view after the following example:
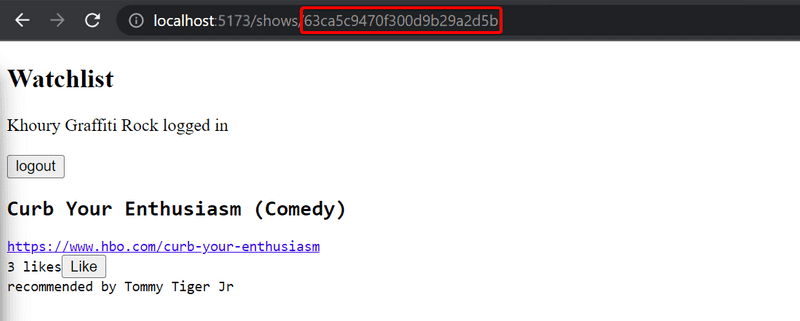
Users should be able to access the view by clicking the name of the show in the view that lists all of the shows.
After you're done with this exercise, the functionality that was implemented in exercise 5.7 is no longer necessary.
Clicking a show no longer needs to expand the item in the list and display the details of the show.
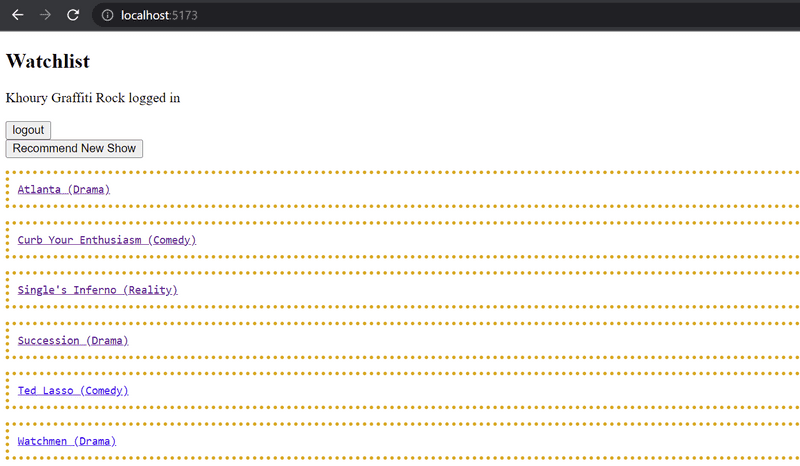
7.17: Navigation
Implement a navigation menu for the application:
7.18: comments, Step 1
Implement the functionality for commenting on recommended shows:
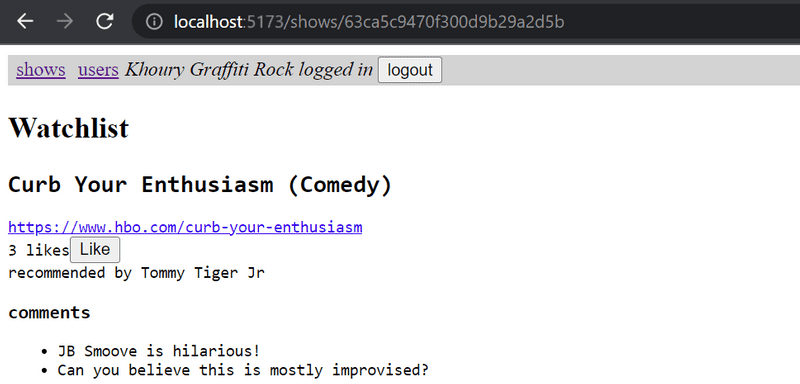
Comments should be anonymous, meaning that they are not associated with the user who left the comment.
In this exercise, it is enough for the frontend to only display the comments that the application receives from the backend.
An appropriate mechanism for adding comments to a show would be an HTTP POST request to the api/shows/:id/comments endpoint.
7.19: comments, Step 2
Extend your application so that users can add comments to recommended shows from the frontend:
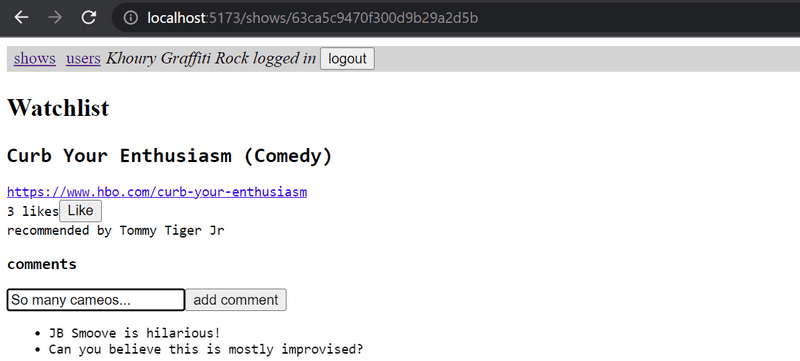
7.20: Styles, Step 1
Improve the appearance of your application by applying one of the methods shown in the course material.
7.21: Styles, Step 2
You can mark this exercise as finished if you use an hour or more for styling your application.
This was the last exercise for this part of the course and it's time to push your code to GitHub if you haven't already and mark the exercises that were completed on Canvas.








