d
Token authentication
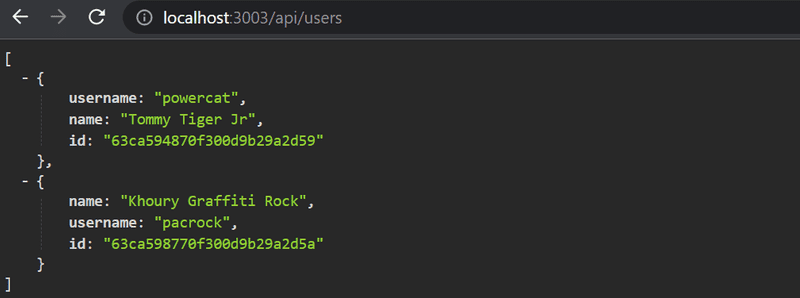
Now that we have created users on the backend, let's move on and add more functionality related to users and their tasks. In particular, users must be able to log into our application, and when a user is logged in, their user information must automatically be attached to any new tasks they create.
Let's start by implementing support for token-based authentication to the backend.
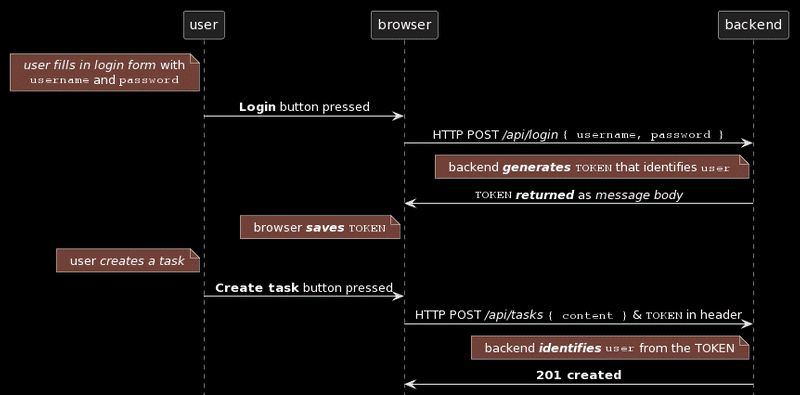
The principles of token-based authentication are depicted in the following sequence diagram:
-
User starts by logging in using a login form implemented with React
- We will add the login form to the frontend in part 5
- This causes the React code to send the username and the password to the server address /api/login as a HTTP POST request.
-
If the username and the password are correct, the server generates a token that somehow identifies the logged-in user.
- The token is signed digitally, making it highly impracticable to falsify cryptographically
- The backend responds with a status code indicating the operation was successful and returns the token with the response.
- The browser saves the token, for example to the state of a React application.
- When the user creates a new task (or does some other operation requiring identification), the React code sends the token to the server with the request.
- The server uses the token to identify the user
Let's first implement the functionality for logging in. Install the jsonwebtoken library, which allows us to generate JSON web tokens.
npm i jsonwebtokenThe code for logging in goes to the file controllers/login.js.
const jwt = require("jsonwebtoken");
const bcrypt = require("bcrypt");
const loginRouter = require("express").Router();
const User = require("../models/user");
loginRouter.post("/", async (request, response) => {
const { username, password } = request.body;
const user = await User.findOne({ username });
const passwordCorrect = user === null
? false
: await bcrypt.compare(password, user.passwordHash);
if (!(user && passwordCorrect)) {
return response.status(401).json({
error: "invalid username or password"
});
}
const userForToken = {
username: user.username,
id: user._id,
};
const token = jwt.sign(userForToken, process.env.SECRET);
response
.status(200)
.send({ token, username: user.username, name: user.name });
});
module.exports = loginRouter;The code starts by searching for the user from the database via the username attached to the request.
const user = await User.findOne({ username });Next, it checks the password, which is also attached to the request.
const passwordCorrect = user === null
? false
: await bcrypt.compare(password, user.passwordHash);Remember that passwords themselves are not saved to the database.
Instead, we store the hashes calculated from the passwords.
This means we need to use bcrypt.compare to check if the password is correct:
await bcrypt.compare(password, user.passwordHash);If the user is not found, or the password is incorrect, we respond to the request with the status code 401 unauthorized. The reason for the failure is explained in the response body.
if (!(user && passwordCorrect)) {
return response.status(401).json({
error: "invalid username or password"
});
}If the password is correct, a token is created with the method jwt.sign.
The token contains the username and the user id in a digitally signed form.
const userForToken = {
username: user.username,
id: user._id,
};
const token = jwt.sign(userForToken, process.env.SECRET);The token has been digitally signed using a string from the environment variable SECRET as the secret.
The digital signature ensures that only parties who know the secret can generate a valid token.
The value for the environment variable must be set in the .env file.
A successful request is responded to with the status code 200 OK. The generated token and the username of the user are sent back in the response body.
response
.status(200)
.send({ token, username: user.username, name: user.name });Now the code for login just has to be added to the application by adding the new router to app.js.
const loginRouter = require("./controllers/login");
//...
app.use("/api/login", loginRouter);Let's try logging in using the WebStorm REST client:
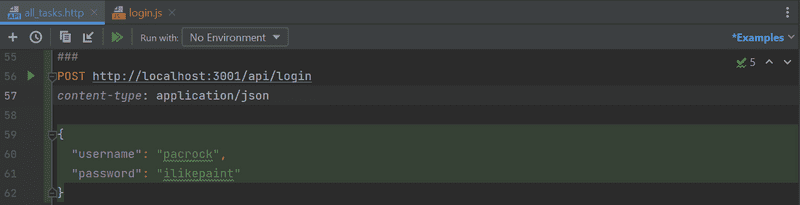
It does not work. The following is printed to the console:
<body>
<pre>Error: secretOrPrivateKey must have a value<br> at module.exports [as sign] (C:\Users\powercat\comp227\part3\tasks-backend\node_modules\jsonwebtoken\sign.js:105:20)<br> at C:\Users\powercat\comp227\part3\tasks-backend\controllers\login.js:25:23</pre>
</body>
...
Response code: 500 (Internal Server Error); Time: 235ms (235 ms); Content length: 387 bytes (387 B)The command jwt.sign(userForToken, process.env.SECRET) fails.
We forgot to set a value to the environment variable SECRET.
It can be any string.
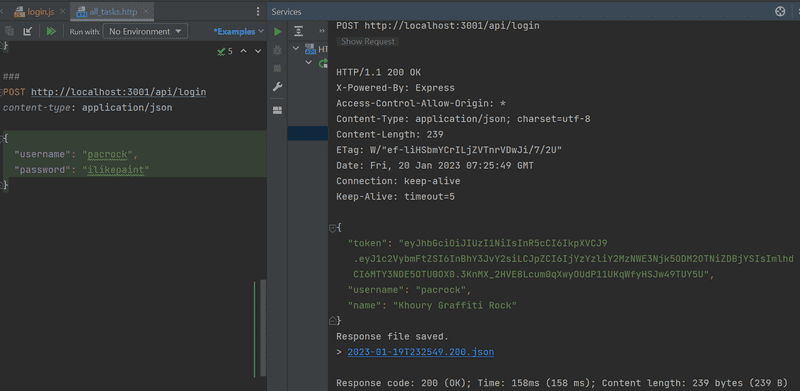
When we set the value in file .env, (and restart the server), the login works.
A successful login returns the user details and the token:
A wrong username or password returns an error message and the proper status code:
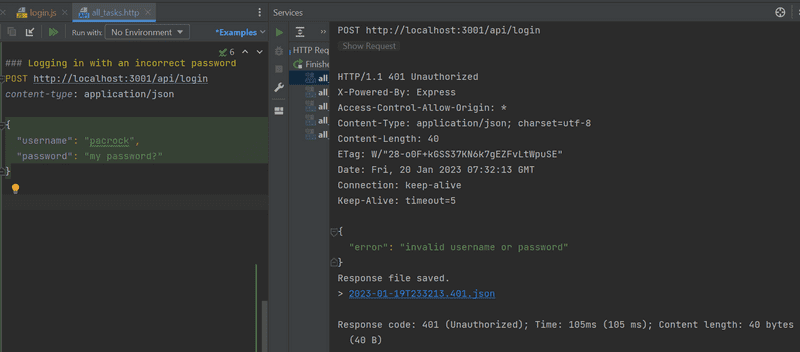
Notice here that I placed a comment after the ### syntax.
This is helpful when you start having a larger test file where you have different scenarios so you can more easily find what you are looking for.
Limiting creating new tasks to logged-in users
Let's change creating new tasks so that it is only possible if the POST request has a valid token attached.
The task is then saved to the tasks list of the user identified by the token.
There are several ways of sending the token from the browser to the server. We will use the Authorization header. The header also tells which authentication scheme is used. This can be necessary if the server offers multiple ways to authenticate. Identifying the scheme tells the server how the attached credentials should be interpreted.
The Bearer scheme is suitable for our needs.
In practice, this means that if the token is, for example,
the string eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9, the Authorization header will have the value:
Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9Our controllers/tasks.js will change like so:
const jwt = require("jsonwebtoken");
// ...
const getTokenFrom = request => { const authorization = request.get("authorization"); if (authorization && authorization.startsWith("Bearer ")) { return authorization.replace("Bearer ", ""); } return null;};
tasksRouter.post("/", async (request, response) => {
const body = request.body;
const decodedToken = jwt.verify(getTokenFrom(request), process.env.SECRET); if (!decodedToken.id) { return response.status(401).json({ error: "token invalid" }); } const user = await User.findById(decodedToken.id);
if (!user) {
return response.status(400).json({ error: "UserId missing or not valid" })
}
const task = new Task({
content: body.content,
important: body.important || false, date: new Date(),
user: user._id
});
const savedTask = await task.save();
user.tasks = user.tasks.concat(savedTask._id);
await user.save();
response.status(201).json(savedTask);
})The helper function getTokenFrom isolates the token from the authorization header.
The validity of the token is checked with jwt.verify.
The method also decodes the token or returns the Object that the token was based on.
const decodedToken = jwt.verify(token, process.env.SECRET);If the token is missing or it is invalid, the exception JsonWebTokenError is raised.
We need to extend the error handling middleware to take care of this particular case:
const errorHandler = (error, request, response, next) => {
if (error.name === "CastError") {
return response.status(400).send({ error: "malformatted id" })
} else if (error.name === "ValidationError") {
return response.status(400).json({ error: error.message })
} else if (error.name === "MongoServerError" && error.message.includes("E11000 duplicate key error")) {
return response.status(400).json({ error: "expected `username` to be unique" })
} else if (error.name === "JsonWebTokenError") { return response.status(401).json({ error: "token invalid" }) }
next(error)
}The object decoded from the token contains the username and id fields, which tell the server who made the request.
If the object decoded from the token does not contain the user's identity (decodedToken.id is undefined),
error status code 401 unauthorized
is returned and the reason for the failure is explained in the response body.
if (!decodedToken.id) {
return response.status(401).json({
error: "token invalid"
});
}When the identity of the maker of the request is resolved, the execution continues as before.
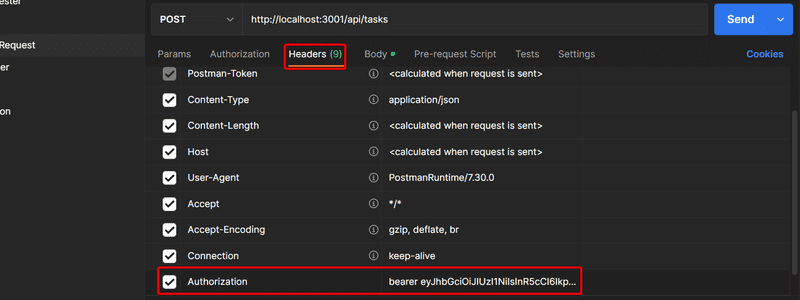
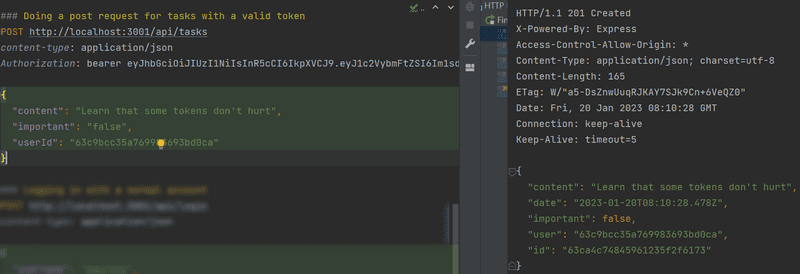
A new task can now be created using a REST client if the authorization header is given the correct value,
something like the string Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9, where the second value is the token returned by the login operation.
Using Postman this looks as follows:
and with the WebStorm REST client
Error handling
Token verification can also cause a JsonWebTokenError.
For example, if we remove a few characters from the token and try creating a new task, this happens:
JsonWebTokenError: invalid signature
at /Users/powercat/comp227/part3/tasks-backend/node_modules/jsonwebtoken/verify.js:126:19
at getSecret (/Users/powercat/comp227/part3/tasks-backend/node_modules/jsonwebtoken/verify.js:80:14)
at Object.module.exports [as verify] (/Users/powercat/comp227/part3/tasks-backend/node_modules/jsonwebtoken/verify.js:84:10)
at tasksRouter.post (/Users/powercat/comp227/part3/tasks-backend/controllers/tasks.js:40:30)Once we get an exception, if we are not running nodemon we may have to restart our program, as any subsequent bad requests could be met with an Internal Server Error (500).
There are many possible reasons for a decoding error.
The token can be faulty (like in our example),
falsified, or expired.
Let's extend our errorHandler in utils/middleware.js to take into account the different decoding errors.
const unknownEndpoint = (request, response) => {
response.status(404).send({ error: "unknown endpoint" });
}
const errorHandler = (error, request, response, next) => {
logger.error(error.message);
if (error.name === "CastError") {
return response.status(400).send({
error: "malformatted id"
});
} else if (error.name === "ValidationError") {
return response.status(400).json({
error: error.message
});
} else if (error.name === "JsonWebTokenError") { return response.status(401).json({ error: "invalid token" }); }
next(error);
};The current application code can be found on GitHub, branch part4-9.
If the application has multiple interfaces requiring identification, JWT's validation should be separated into its own middleware. An existing library like express-jwt could also be used.
Problems of Token-based authentication
Token authentication is pretty easy to implement, but it contains one problem. Once the API user, (e.g. a React app) gets a token, the API has a blind trust with the token holder. What if the access rights of the token holder should be revoked?
There are two solutions to the problem. The easier one is to limit the validity period of a token:
loginRouter.post("/", async (request, response) => {
const { username, password } = request.body;
const user = await User.findOne({ username })
const passwordCorrect = user === null
? false
: await bcrypt.compare(password, user.passwordHash);
if (!(user && passwordCorrect)) {
return response.status(401).json({
error: "invalid username or password"
});
}
const userForToken = {
username: user.username,
id: user._id,
};
// token expires in 60*60 seconds, that is, in one hour
const token = jwt.sign( userForToken, process.env.SECRET, { expiresIn: 60*60 } );
response
.status(200)
.send({ token, username: user.username, name: user.name });
});Once the token expires, the client app needs to get a new token. Usually, this happens by forcing the user to re-login to the app.
The error handling middleware should be extended to give a proper error in the case of an expired token:
const errorHandler = (error, request, response, next) => {
logger.error(error.message);
if (error.name === "CastError") {
return response.status(400).send({ error: "malformatted id" });
} else if (error.name === "ValidationError") {
return response.status(400).json({ error: error.message });
} else if (error.name === "MongoServerError" && error.message.includes("E11000 duplicate key error")) {
return response.status(400).json({
error: "expected `username` to be unique"
});
} else if (error.name === "JsonWebTokenError") {
return response.status(401).json({
error: "invalid token"
});
} else if (error.name === "TokenExpiredError") { return response.status(401).json({ error: "token expired" }); }
next(error);
}The shorter the expiration time, the safer the solution is. If the token falls into the wrong hands or user access to the system needs to be revoked, the token is only usable for a limited amount of time. However, a short expiration time forces a potential pain for the user, as it requires them to log in more frequently.
The other solution is to save info about each token to backend database and to check for each API request if the access right corresponding to the token is still valid. With this scheme, access rights can be revoked at any time. This kind of solution is often called a server-side session.
The negative aspect of server-side sessions is the increased complexity in the backend and also the effect on performance since the token validity needs to be checked for each API request to the database. Database access is considerably slower compared to checking the validity of the token itself. That is why it is quite common to save the session corresponding to a token to a key-value database such as Redis that is limited in functionality compared to a MongoDB or a relational database but extremely fast in some usage scenarios.
When server-side sessions are used, the token is a random string (quite often). The token does not include any information about the user as it is quite often the case when jwt-tokens are used. For each API request, the server fetches the relevant information about the identity of the user from the database. It is also quite usual that instead of using Authorization-header, cookies are used as the mechanism for transferring the token between the client and the server.
End tasks
There have been many changes to the code which have caused a typical problem for a fast-paced software project: most of the tests have broken. Because this part of the course is already jammed with new information, we will leave fixing the tests to a non-compulsory exercise.
Usernames, passwords and applications using token authentication must always be used over HTTPS. We could use a Node HTTPS server in our application instead of the HTTP server (it requires more configuration). On the other hand, the production version of our application is on Render, so our application stays secure. Render routes all traffic between a browser and the Render server over HTTPS.
We will implement login to the frontend in the next part.